CAROTID ARTERY ULTRASOUND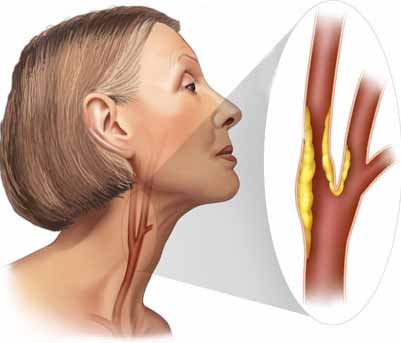
What is a carotid artery ultrasound?
Carotid arteries supply blood to the brain. Atherosclerosis (arterial plaque) may develop in these arteries and increase the risk of stroke. A carotid artery ultrasound uses sound waves that are directed at the blood vessels of the neck and enables the cardiologist to look at blood flow in these vessels that supply the brain to identify any significant plaque or blockages. This technique allows us to image the carotid arteries to determine location and severity of narrowing of these blood vessels.
How is the test performed?
You will be asked to lie flat on a cushioned examination imaging table. Our registered vascular technologist will apply an ultrasound probe over the neck to evaluate the carotid arteries. Using a medical gel, the imaging probe will image the vascular structures of the neck. The images are displayed on a medical monitor for Dr. Marini. The carotid ultrasound often takes 45 minutes for the average examination, although it may take longer depending on the findings of the ultrasonographer.
What preparation is required?
No special preparation is required. Patients are allowed to eat or drink prior to the test. Patients can continue to take their medications. If you require oxygen to lie down, we request that you bring oxygen so you’re comfortable during the procedure.
What are some of the indications that require a carotid ultrasound?
- A carotid ultrasound is often used to evaluate asymptomatic carotid bruit identified on the physical examination.
- Carotid ultrasound is recommended in patients who have had a recent stroke to determine the cause of the stroke.
- Carotid ultrasound is used to evaluate a symptomatic carotid bruit.
- Carotid ultrasound is helpful in patients with known carotid disease. The routine monitoring of patients and the frequency of patient monitoring is dictated by national guidelines.
- Carotid ultrasound is commonly used to evaluate a transient ischemic attack (TIA).
- Carotid ultrasound is helpful when patients develop new neurologic symptoms such as weakness on one side of the face, slurred speech, optic neuropathy, arterial occlusion seen on retinal examination, ocular microembolism, weakness of a limb, etc.
- Carotid ultrasound is recommended when patients eye doctor determines that there is a presence of Hollenhorst plaques (retinal arterial emboli), amaurosis fugax is the cause of transient monocular blindness and is a strong indication for performing a carotid ultrasound. Subclavian steal syndrome is caused by subclavian stenosis and requires carotid ultrasound evaluation with imaging of the vertebral arteries when possible.
- When there’s been blunt neck trauma or injury of the carotid artery, carotid ultrasound is necessary.
- Patients who have recurrent cerebrovascular disease may require a repeat carotid examination.
- Patients who have suspected carotid dissection require carotid ultrasound.
- Patients with suspected aneurysm of the carotid artery require carotid ultrasound.
- Some patients who have had carotid stenting or carotid endarterectomy often require a carotid ultrasound for followup evaluations.
- Patients who have a pulsatile neck mass can have it further evaluated with carotid ultrasound.
- Patients who require major cardiovascular surgical procedures require carotid ultrasound in order to minimize potential complications.
